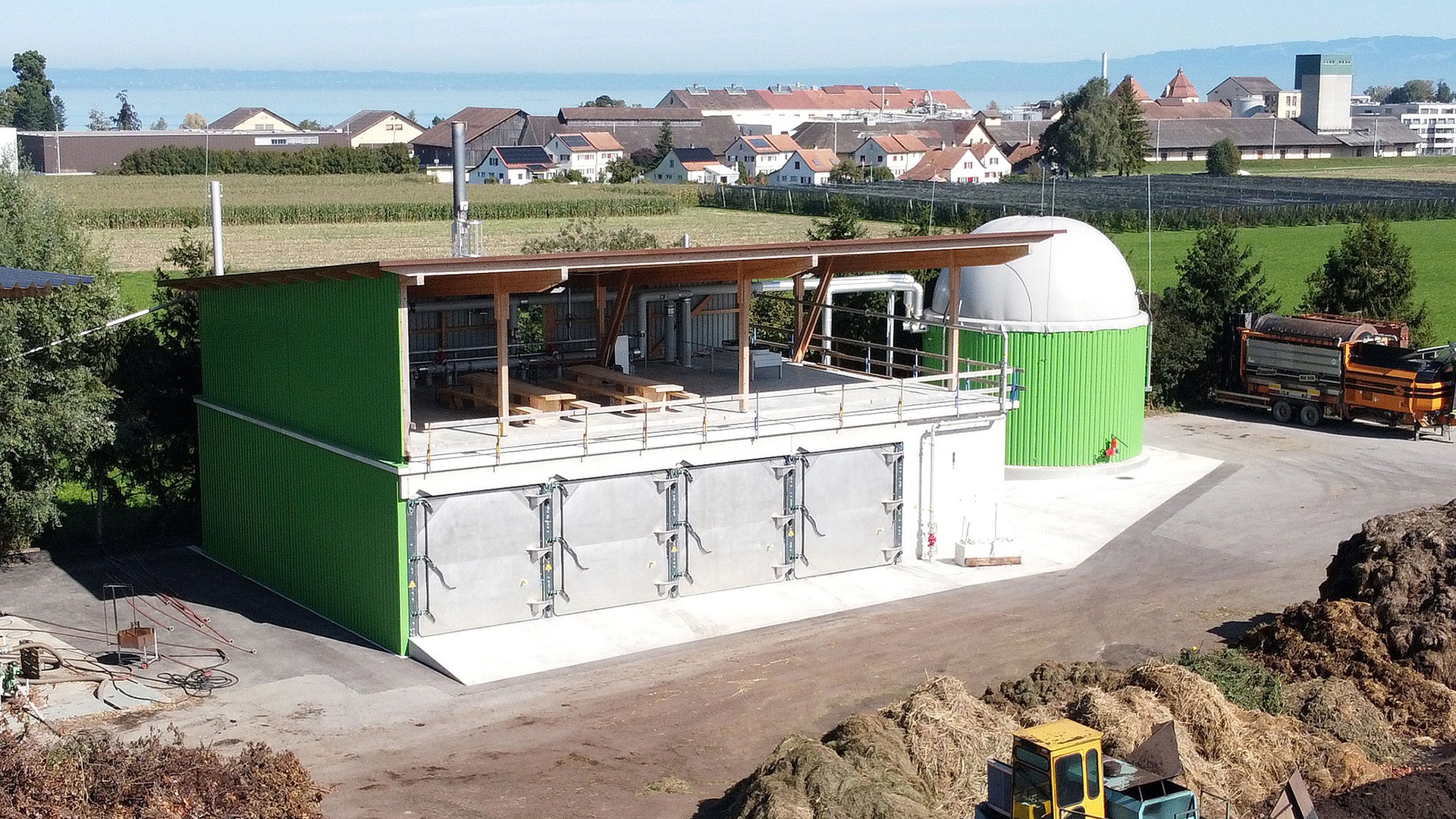
A solid waste fermentation biogas plant is being installed near Patiala, India, which will treat cattle manure and rice straw, recovered within a maximum radius of 5 km. Renergon’s solid waste fermentation (dry digestion in fermenter boxes) does not require a mixable and pumpable substrate liquid blend, which greatly minimizes the need for water when utilizing organic waste.
The biogas produced is to be processed into bio-CNG (compressed natural gas) through gas treatment and stored in gas cylinders. The use of rice straw mitigates the massive disposal problem on site (burning straw in the fields) and thus ensures a huge improvement in air quality. Furthermore, a valuable multi-nutrient and humus fertilizer is produced in the form of marketable composts.
Swiss Contribution to Biogas in India
Founded in 2010, Renergon International Ltd. has proven experience in solid waste fermentation. The entire project planning and plant design, as well as the biogas plant’s construction supervision and commissioning are ensured by Renergon, in close cooperation with „Cities Innovative Biofuels Ltd.“, the Indian partner. In addition, the knowledge sharing and technology transfer take place through the education and training of the partner company’s employees.
The technology of the Renergon RSD plants starts where conventional liquid biogas and plug flow systems reach their limits. Dry fermentation allows for the production of dry, fibrous substrates that often cause issues in other types of systems; however, with this process running batch-wise it is able to provide you a continual yield without any issue whatsoever.
Biogas, a clean and versatile energy source, can be transported to where it is needed. It has the ability not only generate electricity and heat using combined heat-and power units (CHP), but also biomethane which may then either serve as fuel for cars (CNG), industrial commercial use or for cooking systems within households.
Read more on REPIC
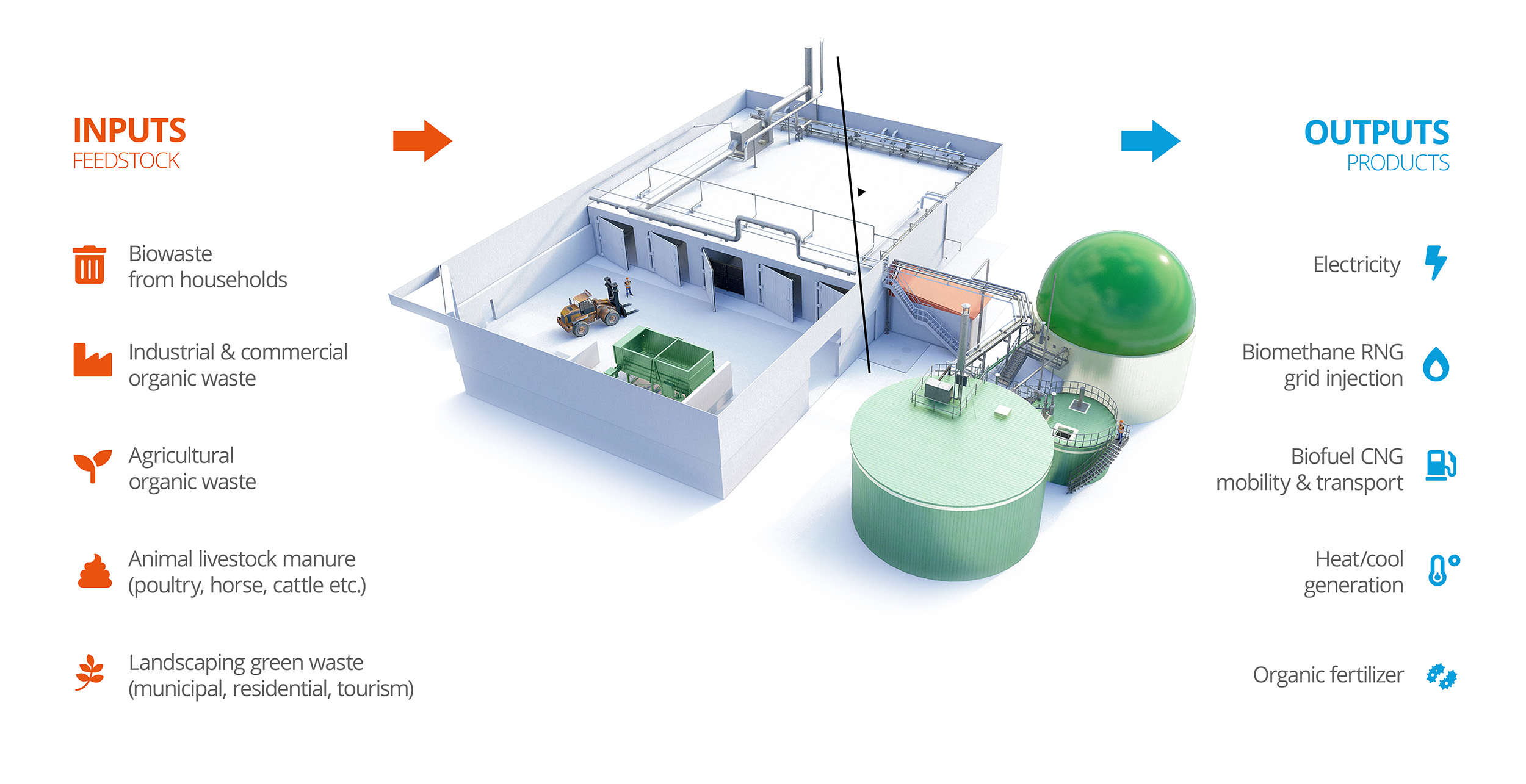
Dry Anaerobic Digestion for Biogas
The remarkable success of this biogas project in India owes its achievements to the power of collaboration. One notable partnership worth mentioning is the dynamic alliance between BioShakti (India) and Renergon (Switzerland), which has received invaluable support from a REPIC grant courtesy of the Swiss federal government. Together, they are pioneering a transformative initiative in Patiala, Punjab, aimed at combatting the alarming practice of rice straw burning in the region.
In the heart of Patiala, a cutting-edge solid waste fermentation facility is taking shape, designed to co-process cattle manure and rice straw using Renergon’s state-of-the-art solid waste fermentation system. What sets this innovative approach apart is its ability to operate without the need for a liquid substrate, thus significantly reducing water consumption. The inclusion of rice straw in this fermentation process not only eliminates field burning but also leads to remarkable improvements in air quality.
Biogas in India: A Conclusive Solution
The pervasive issue of open-field rice straw burning in India has long been a devastating environmental crisis, inflicting severe consequences in the form of air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and health risks. However, the introduction of biogas production, particularly through the dry anaerobic digestion technology, presents a sustainable remedy to this urgent problem. By conserving precious water resources, enhancing air quality, and producing clean energy, these biogas endeavors symbolize a beacon of hope for a cleaner and healthier India. Collaborative partnerships and pioneering initiatives like the one in Patiala, Punjab, are paving the way for a more radiant and sustainable future. The time has come to challenge the practice of rice straw burning and wholeheartedly embrace biogas as a cleaner, eco-friendly alternative.
The transformative potential of biogas technology in India’s agricultural regions cannot be understated. With a substantial volume of organic waste stemming from animal dung, crop remnants, and agricultural byproducts, biogas technology emerges as an eco-friendly and sustainable solution. It not only offers a clean and cost-effective energy source but also effectively tackles critical environmental issues, including air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and soil degradation. By harnessing the power of biogas, farmers can convert waste into invaluable resources like biofuel, organic fertilizers, and compost, enriching soil quality and bolstering agricultural yields. Furthermore, biogas production diminishes reliance on fossil fuels, mitigates climate change, and fosters a greener and healthier future for India’s agricultural communities.






