Proper horse manure management is a crucial aspect of running an equestrian facility or keeping horses. Not only does it contribute to a clean and healthy environment for the horses and their caretakers, but it also plays a significant role in preserving our natural surroundings. With the average horse producing between 40 and 50 pounds (ca. 23 kg) of manure daily, the challenge of managing this waste cannot be underestimated.
This blog post explores effective and sustainable methods for horse manure disposal, offering practical solutions for horse farm owners, equestrian center managers, and individual horse keepers alike.
Understanding Horse Manure
Horse manure consists of bedding material, undigested fiber, and nutrients, making it a significant environmental concern if not disposed of correctly. When left unmanaged, it can contaminate water sources, contribute to the spread of parasites, and emit unpleasant odors. However, with proper management, horse manure can be transformed from waste to a valuable resource. The daily manure output from a single horse can seem daunting, but understanding its composition and impact is the first step towards effective disposal and utilization.
Method 1: Composting
Composting is a highly beneficial method for managing horse manure. It involves the biological decomposition of organic matter under controlled conditions to produce a nutrient-rich soil amendment. For equestrian facilities, composting not only reduces the volume of waste but also transforms it into a valuable product that can improve soil health and fertility.
How to Compost Horse Manure
- Start your compost pile by mixing horse manure with carbon-rich materials such as straw, sawdust, or leaves. This balance helps to accelerate the decomposition process.
- Maintain moisture and aeration by turning the pile regularly. This ensures even decomposition and prevents the development of foul odors.
- Monitor the temperature of your compost pile, which should heat up to 130-150°F (55-65°C) to effectively kill weed seeds and pathogens.
Composted manure is excellent for gardening and landscaping, offering a sustainable solution to manure management.
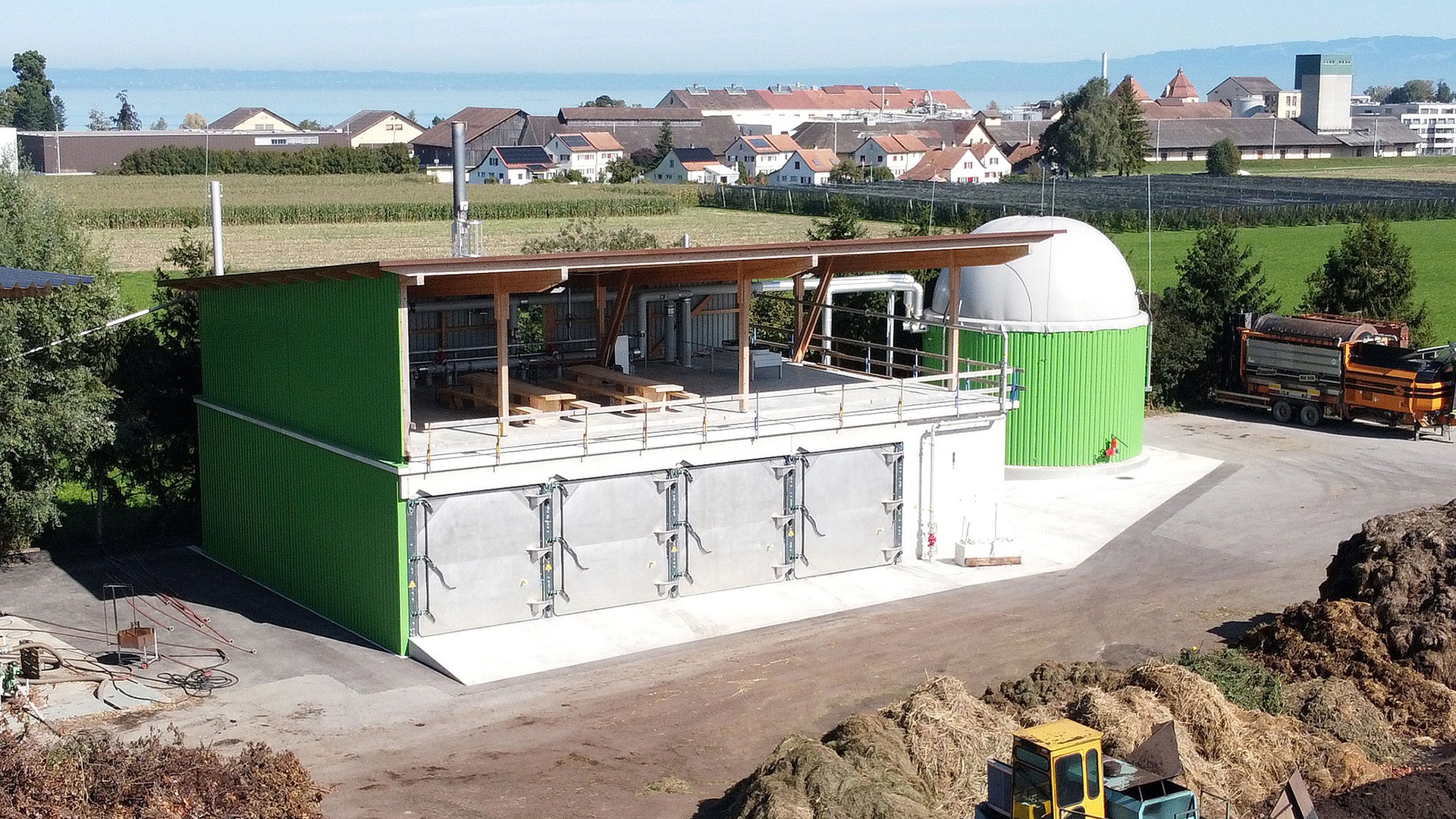
Method 2: Biogas Production
Turning horse manure into biogas is an innovative and eco-friendly method. Biogas production involves anaerobic digestion, where microorganisms break down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, producing methane-rich gas that can be used for energy.
Setting Up a Biogas Digester
- Compact-scale digesters can be suitable for individual farms, whereas larger operations may require industrial-scale systems.
- Consider the investment in terms of initial setup costs and ongoing maintenance to ensure it’s a viable option for your facility.
Biogas production from manure not only provides a renewable source of energy, but also significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
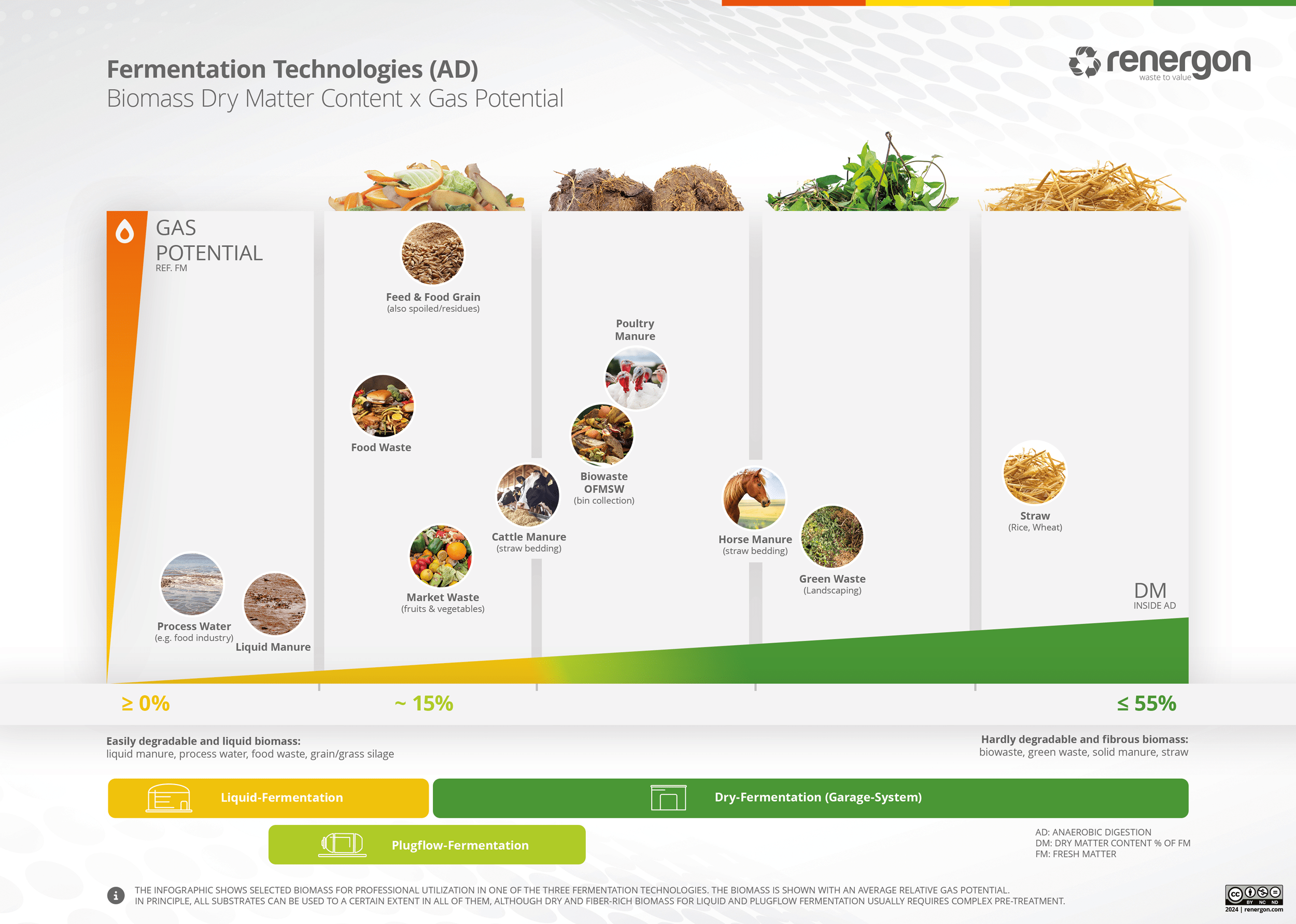
Method 3: Horse Manure Spreading
Manure spreading is another method used by horse owners, especially those with access to large agricultural lands. This practice involves evenly distributing manure over fields to act as a natural fertilizer.
Considerations for Manure Spreading
- Timing and rate are crucial to prevent nutrient runoff into waterways. It’s best to spread manure in dry conditions and well before heavy rains are expected.
- Soil testing can help determine the nutrient needs of your fields, ensuring that manure is used in a way that complements the soil’s existing nutrient profile without leading to over-fertilization.
Manure spreading requires adherence to local environmental regulations to mitigate the impact on water quality and surrounding ecosystems.
Method 4: Removal Services
For those who cannot manage manure on-site, professional removal services offer a convenient solution. These services collect and dispose of or repurpose manure, ensuring that it is handled in an environmentally responsible manner.
Benefits of Removal Services
- Convenience and efficiency for facilities without the space or resources to manage manure on-site.
Diverse disposal options, as many removal services compost the manure or use it for energy production, contributing to a sustainable cycle.
Conclusion
In the realm of horse manure management, transforming this by-product into a valuable resource is not only an act of environmental stewardship but also a step towards sustainable energy production. Among the various disposal methods discussed, biogas production via solid matter fermentation stands out as the most holistic and sustainable solution. This technology excels by utilizing solid, stackable biomass—such as horse manure—in a manner that is both energy-efficient and reliable.
The compact biogas solution offered by Renergon is a testament to the practicality and viability of this approach. Requiring a minimum of approximately 10,000 tons of biomass to achieve economic sensibility, it’s clear that the scale of the operation significantly influences its feasibility and profitability. This threshold, however, is subject to variation based on specific local conditions and available land. It underscores a crucial point: the larger the scale of the biogas project, the better its economic and environmental returns.
Choosing the path of biogas production not only addresses the pressing issue of manure management in a responsible manner but also contributes to the global need for renewable energy sources. By adopting solid matter fermentation technologies, equestrian facilities can transform a waste management challenge into an opportunity for sustainable development and energy independence. This approach aligns with a broader vision of eco-friendly agriculture and energy production, promising a cleaner, greener future for our communities and the planet.






